Below are the step by step comprehensive Instructions for subroutine CA migration from Windows Server 2003 to Windows Server 2008 R2.
This article is published in three parts and in this part we will discuss more in details on about preparing of source and destination server for the migration
1. Preparing Source Server
Map network share in source server to copy backup files
Perform/Verify System state backup of Source CA
a. Verify and backup CA Template set
Open Command prompt
Type certutil.exe – catemplates > catemplates.txt
Verify the contents of catemplates.txt with the templates displayed in Certificate Authority snap-in
b. Verify and backup CA’s CSP and signature algorithm
Open Command prompt
Type certutil.exe –getreg ca\csp\* > csp.txt
Verify that the csp.txt contains CSP detaill
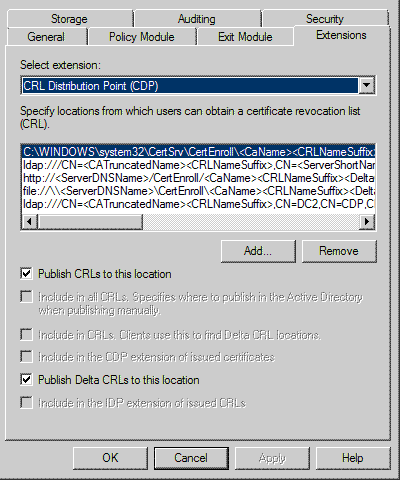
c. Publish CRL with extended validity period
Open Certificate Authority snap in
In the console tree right click “Revoked Certificates” and click Properties
Record the current CRL Publishing Parameters
Set the CRL Delta publishing interval to 2 days
Click on “Revoked Certificates” -> all task -> publish -> Delta CRL only
d. Backup CA DB and Private Key
Map shared network drive to take the backup
on Certificate authority snap-in right click point to All task and backup CA
On the Welcome page of the CA Backup wizard, click Next.
On the Items to Back Up page, select the Private key and CA certificate and Certificate database and certificate database log check boxes, specify the backup location, and then click Next.
On the Select a Password page, type a password to protect the CA private key, and click Next.
On the Completing the Backup Wizard page, click Finish.
After the backup completes, verify the following files in the location you specified CAName.p12 containing the CA certificate and private key Database folder containing files certbkxp.dat, edb#####.log, and CAName.edb
Open command prompt and type Net stop Certsvc to stop Certificate Service
e. Backup CA Registry
Click Start, point to Run, and type regedit to open the Registry Editor.
In HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\CertSvc, right-click Configuration, and then click Export.
Specify a location and file name, and then click Save. This creates a registry file containing CA configuration data from the source CA.
f. Remove source server
Launch Add or remove program
Click Add/Remove windows components and uncheck Certificate Services
Click next and finish
Remove source server from domain
Delete AD computer object
Rename source server to some temp name
2. Preparing Destination Server
Change destination server name to the initial source server name
Add destination server to domain
Map network share used in taking the backup on source server
a. Import the CA certificate
Start the Certificates snap-in for the local computer account.
In the console tree, double-click Certificates (Local Computer), and click Personal.
On the Action menu, click All Tasks, and then click Import to open the Certificate Import Wizard. Click Next.
Locate the <CAName>.p12 file created by the CA certificate and private key backup on the source CA, and click Open.
Type the password, and click OK.
Click Place all certificates in the following store.
Verify Personal is displayed in Certificate store. If it is not, click Browse, click Personal, and click OK.
b. Add CA and IIS roles on destination server
Log on to the destination server, and start Server Manager.
In the console tree, click Roles.
On the Action menu, click Add Roles.
If the Before you Begin page appears, click Next.
On the Select Server Roles page, select the Active Directory Certificate Services and Web Server (IIS) check box, and click Next.
On the Introduction to AD CS page, click Next.
On the Role Services page, click the Certification Authority check box, and Certification Authority Web Enrollment and click Next.
On the Specify Setup Type page, specify either Enterprise and click Next.
On the Specify CA Type page, select Subordinate CA, and click Next.
On the Set Up Private Key page, select Use existing private key and Select a certificate and use its associated private key.
In the Certificates list, click the imported CA certificate, and then click Next.
On the Configure Certificate Database page, specify the locations for the CA database and log files.
On the Confirm Installation Selections page, review the messages, and then click Install.
Hope you liked this article, please continue with the next part where we will discuss in details of the below
Part 2 – Restoring the Source from backups and Verifying the migration
Part 3 – Back Out procedure